when to treat
Last edited 04/2022 and last reviewed 05/2022
Starting antihypertensive drug treatment
Offer antihypertensive drug treatment in addition to lifestyle advice to adults of any age with persistent stage 2 hypertension. Use clinical judgement for people of any age with frailty or multimorbidity
Discuss starting antihypertensive drug treatment, in addition to lifestyle advice, with adults aged under 80 with persistent stage 1 hypertension who have 1 or more of the following:
- target organ damage
- established cardiovascular disease
- renal disease
- diabetes
- an estimated 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease of 10% or more.
- Use clinical judgement for people with frailty or multimorbidity
Consider antihypertensive drug treatment in addition to lifestyle advice for people aged over 80 with a clinic blood pressure of over 150/90 mmHg. Use clinical judgement for people with frailty or multimorbidity
Measure standing as well as seated blood pressure in people with hypertension and:
- with type 2 diabetes or
- with symptoms of postural hypotension or
- aged 80 and over.
- in people with a significant postural drop or symptoms of postural hypotension, treat to a blood pressure target based on standing blood pressure
Offer people with isolated systolic hypertension (systolic blood pressure 160 mmHg or more) the same treatment as people with both raised systolic and diastolic blood pressure
For adults with hypertension aged under 80, reduce clinic blood pressure to below 140/90 mmHg and ensure that it is maintained below that level.
For adults with hypertension aged 80 and over, reduce clinic blood pressure to below 150/90 mmHg and ensure that it is maintained below that level. Use clinical judgement for people with frailty or multimorbidity
Summary guidance from NICE (1):
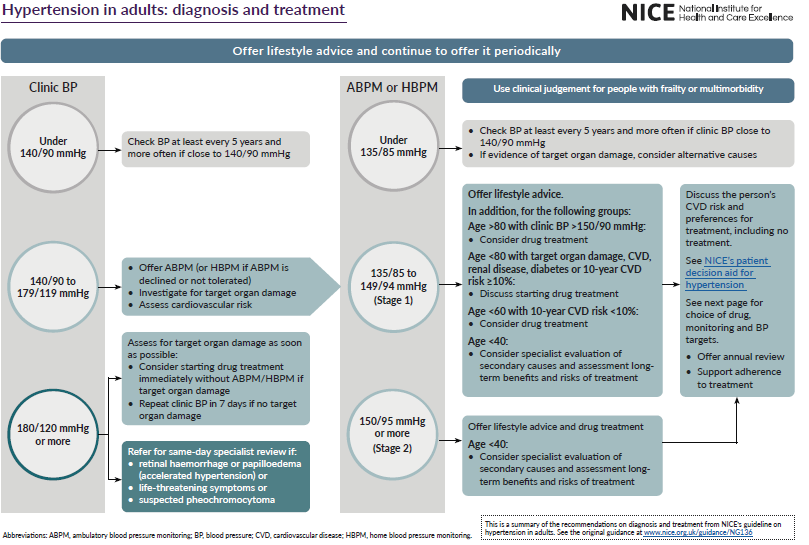

Stage 1 hypertension
- clinic blood pressure ranging from 140/90 mmHg to 159/99 mmHg and subsequent ABPM daytime average or HBPM average blood pressure ranging from 135/85 mmHg to 149/94 mmHg
Stage 2 hypertension
- clinic blood pressure of 160/100 mmHg or higher but less than 180/120 mmHg and subsequent ABPM daytime average or HBPM average blood pressure of 150/95 mmHg or higher
Stage 3 or severe hypertension
- clinic systolic blood pressure of 180 mmHg or higher or clinic diastolic blood pressure of 120 mmHg or higher.
The evidence for treatment (systolic > 160 mm Hg, diastolic > 90 mm Hg) derives from the:
- SHEP - Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Trial - JAMA 1991 - reduction in strokes by 36% and non-fatal MI by 27%
- MRC trial - BMJ 1992 - reduction of strokes by 25% and a 17% reduction in cardiovascular events
- STOP - Swedish Trial in Old Patients - blood pressure reduction resulted in a reduction of stroke by 47% and cardiovascular events by 40%
Reference: