features of non-accidental injury (injury that should raise concerns) in a child in comparison to features suggestive of an accidental injury in a child
Last edited 07/2020
The assessment of any physical injury involves three stages:
-
evaluating the injury itself, its extent, site and any particular patterns
-
taking a history to understand how and why the injury occurred and whether the findings match the story given
- exploring the broader picture (e.g. the child's behaviour, the parent-child interaction, underlying risk factors or markers of emotional abuse or neglect)
Types of injury:
- bruising
- burns
- bite marks
- eye injuries
- bone fractures
- abrasions and lacerations
- intra-oral injuries
Typical features of accidental injuries
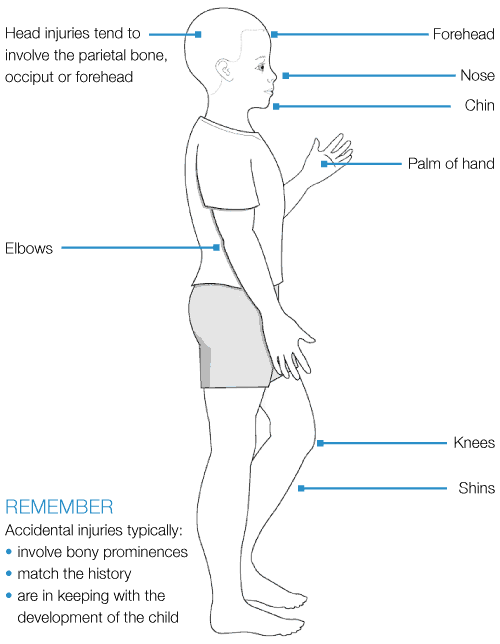
Typical features of non-accidental injuries (injuries that should raise concerns)
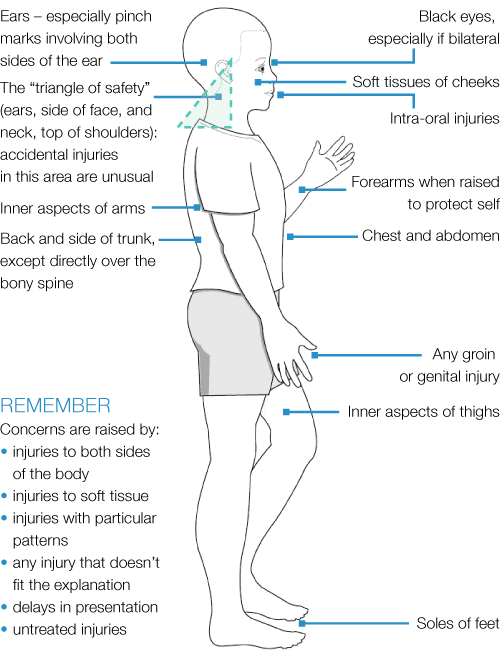
Figures reproduced with permission from Harris J, Sidebotham P, Welbury R et al. Child protection and the dental team: an introduction to safeguarding children in dental practice. COPDEND: Sheffield, 2006/2013, www.bda.org/childprotection
For detailed description of the types of non-accidental injuries then see
https://bda.org/childprotection/Recognising/Pages/Physical.aspx