obesity and combined oral contraceptive (COC) pill and risk of cardiovascular disease
Last edited 06/2020 and last reviewed 05/2021
- a combined pill containing a low dose of oestrogen (i.e. 30 mcg) is indicated
in women who have migraines without auras - this is because the risk of stroke
is greater the higher the dose of oestrogen in the combined pill
- a DTB review (1) suggested that low-dose pill can also be given to women
who have migraines without auras but have one additional risk factor for stroke
- however the review emphasises that these patients must be followed up carefully
- prescribing decisions, with respect to combined hormonal contraception, are made based on the UKMEC criteria below which define migraine with an aura as an absolute contraindication to combined hormonal contraception - see below for further details and guidance with respect to different migraine scenarios
UKMEC Criteria state:
Cardiovascular factors (including migraine) and UKMEC categories (3):
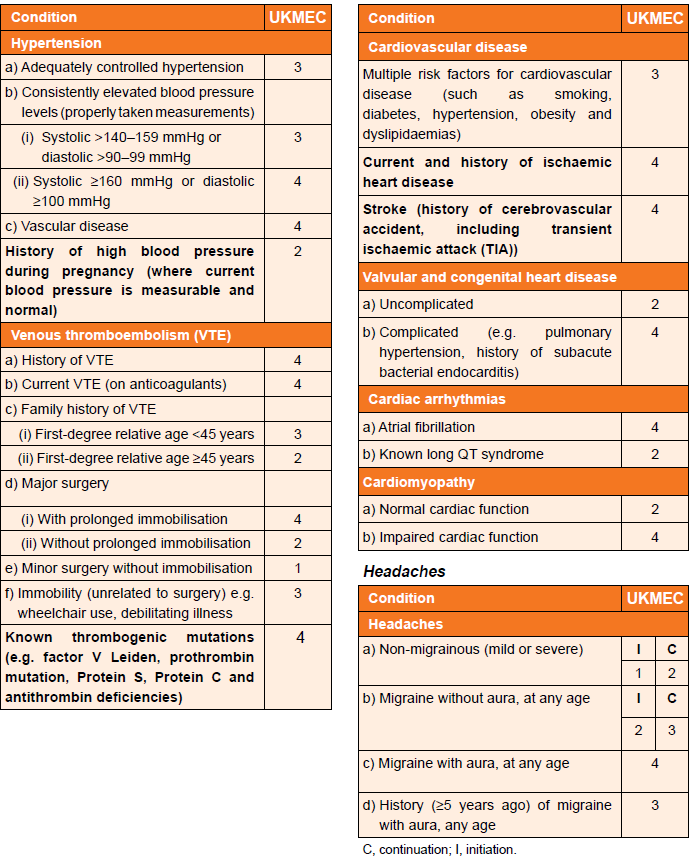
In consideration of UKMEC criteria and combined hormonal contraception (CHC):

Check the summary of product characteristics before prescribing any combined oral contraceptive pill.
Reference:
- (1) Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin (2000), 38 (1), 1-4.
- (2) BNF 7.3
- (3) FSRH Clinical Guideline: Combined Hormonal Contraception (January 2019, Amended July 2019)
migraine and the combined oral contraceptive pill
combined oral contraceptive pill
relative risk of myocardial infarction (smoking, COC)
hypertension and the oral contraceptive pill
combined contraceptive pill and obesity
UKMEC (UK Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use) criteria
general contraindications to combined oral hormonal contraceptive