history taking in children with constipation
Last reviewed 01/2018
Establish during history-taking whether the child or young person has constipation.
Two or more findings from the table below indicate constipation:
| Key components |
Potential findings in a child younger than 1 year |
Potential findings in a child/young person older than 1 year |
| Stool patterns |
- fewer than three complete stools per week (type 3 or 4, see Bristol
Stool Form Scale) this does not apply to exclusively breastfed babies
after 6 weeks of age)
- hard large stool
- 'rabbit droppings' (type 1, Bristol Stool Form Scale)
|
- fewer than three complete stools per week (type 3 or 4, see Bristol
Stool Form Scale)
- overflow soiling (commonly very loose [no form], very smelly [smells
more unpleasant than normal stools], stool passed without sensation.
Can also be thick and sticky or dry and flaky.) "
- 'rabbit droppings' (type 1 Bristol Stool Form Scale )
- large, infrequent stools that can block the toilet
|
| Symptoms associated with defecation |
- distress on stooling
- bleeding associated with hard stool
- straining
|
- poor appetite that improves with passage of large stool
- waxing and waning of abdominal pain with passage of stool
- evidence of retentive posturing: typical straight legged, tiptoed,
back arching posture
- straining
- anal pain
|
| History |
- previous episode(s) of constipation
- previous or current anal fissure
|
- previous episode(s) of constipation
- previous or current anal fissure
- painful bowel movements and bleeding associated with hard stools
|
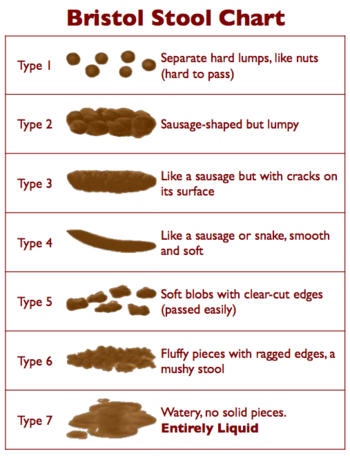
Bristol Stool Scale or Bristol Stool Chart is a medical aid designed to classify
the form of human faeces into seven categories. Sometimes referred to in the
UK as the "Meyers Scale", it was developed by Heaton at the University of Bristol
and was first published in the Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology in 1997)
- form of the stool depends on the time it spends in the colon
- Types 1 and 2 indicate constipation, with 3 and 4 being the "ideal stools"
especially the latter, as they are the easiest to pass, and 5-7 being
further tending towards diarrhoea or urgency.
Reference:
Related pages:
constipation in children
history taking in children (to discriminate features suggestive of idiopathic constipation or other causes)
